CSC110Y
Assignment 1 - September 28, 2022
Image Data Manipulation
Total Mark 49.5 / 50 (99%)
In this assignment, I worked on image data manipulation using Python. I explored the use of various functions and data types in Python, debugged a small Python program, and practiced simple image manipulations such as cropping and applying colour filters.

Handout
Assignment 2 - October 12, 2022
Predicate Logic and Wordle
Total Mark 48.72 / 50 (97.44%)
The focus of this assignment was on predicate logic and wordle. I utilized predicate logic, if statements, and tabular data to simplify if statements and prove mathematical statements. Additionally, I modeled a new problem domain using definitions that translate to Python functions.

Handout
Assignment 3 - November 2, 2022
Loops, Mutation, Applications: Chaos, Fractals, Point Sequences
Total Mark 40.6 / 50 (81.2%)
This assignment involved working with loops, mutation, and applications such as chaos, fractals, and point sequences. I utilized data classes, loops, and mutation in data analysis, sentiment analysis, and interactive visualizations of 2-D point sequences.

Handout
Assignment 4 - November 23
Number Theory, Cryptography, Algorithm Running Time Analysis
Total Mark 50 / 50 (100%)
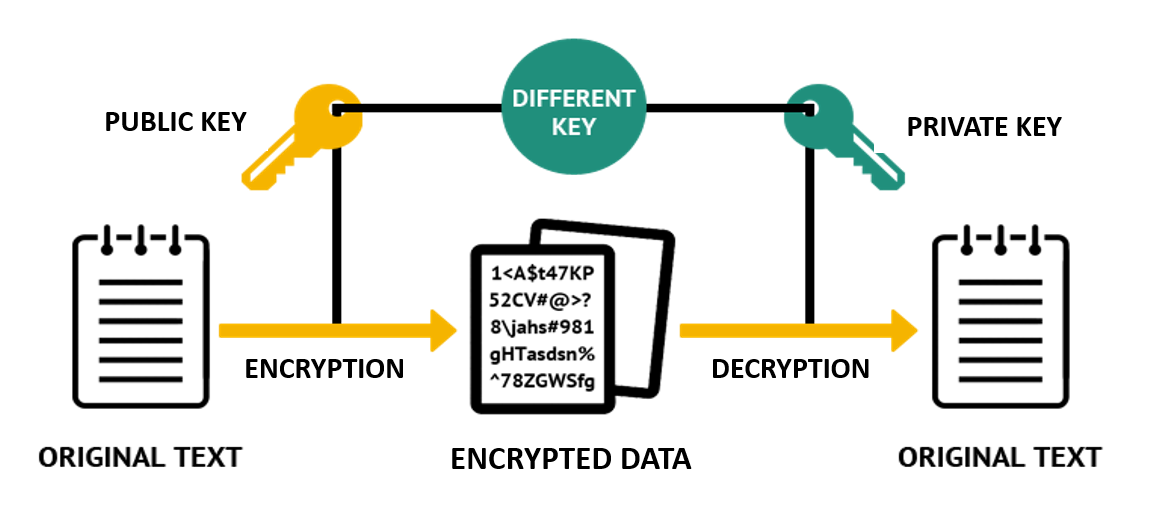
In this assignment, I delved into number theory, cryptography, and algorithm analysis. I worked on proving mathematical statements, analyzing the running time of functions, and extending the RSA public-key cryptosystem.
Handout
What I've Learned
Below are some materials that I learned from CSC110. For additional information, please visit Course Notes.
1. Working with Data
1.1 Introducing the Python Programming Language
1.2 Using the Python Console
1.3 Representing Data I: Numbers
1.4 Representing Data II: Booleans and Strings
1.5 Representing Data III: Collections
1.6 Storing Data in Variables
1.7 Building Up Data with Comprehensions
1.8 Application: Representing Colour
2. Functions
2.1 Python’s Built-In Functions
2.2 Defining Our Own Functions
2.3 Local Variables and Function Scope
2.4 Methods: Functions Belonging to a Data Type
2.5 Importing Python Modules
2.6 Type Conversion Functions
2.7 The Function Design Recipe
2.8 Testing Functions I: doctest and pytest
2.9 Application: Representing Text
3.1 Propositional Logic
3.2 Predicate Logic
3.3 Filtering Collections
3.4 If Statements: Conditional Code Execution
3.5 Simplifying If Statements
3.6 The Main Block: if name == 'main'
3.7 Logical Statements with Multiple Quantifiers
4. Function Specification and Correctness
4.1 Specifying What a Function Should Do
4.2 Type Annotations Revisited
4.3 Checking Function Specifications with python_ta
4.4 Testing Functions II: hypothesis
4.5 Justifying Correctness (Beyond Using Test Cases)
4.6 Proofs and Programming I: Divisibility
4.7 Proofs and Programming II: Prime Numbers
4.8 Application: Linear Regression
5. Working with Complex Data
5.1 Tabular Data
5.2 Defining Our Own Data Types, Part 1
5.3 Defining Our Own Data Types, Part 2
5.4 Repeated Execution: For Loops
5.5 For Loop Variations
5.6 Index-Based For loops
5.7 Nested For Loops
5.8 PythonTA and Accumulation Tables
6. Modifying Values and Variables
6.1 Variable Reassignment, Revisited
6.2 Objects and Object Mutation
6.3 Mutable Data Types
6.4 The Full Python Memory Model: Introduction
6.5 Aliasing and “Mutation at a Distance”
6.6 The Full Python Memory Model: Function Calls
6.7 Testing Functions III: Testing Mutation
7. Number Theory: Theorems, Proofs, and Algorithms
7.1 Introduction to Number Theory
7.2 Greatest Common Divisor
7.3 Proofs and Algorithms III: Computing the Greatest Common Divisor
7.4 Modular Arithmetic
7.5 Modular Exponentiation and Order
8. Case Study: Cryptography
8.1 Introduction to Cryptography
8.2 The One-Time Pad and Perfect Secrecy
8.3 Computing Shared Secret Keys
8.4 The RSA Cryptosystem
8.5 Implementing RSA in Python
8.6 Application: Securing Online Communications
9. Analyzing Algorithm Running Time
9.1 Introduction to Running Time Analysis
9.2 Comparing Asymptotic Function Growth: Big-O Notation
9.3 Big-O, Omega, Theta
9.4 Asymptotic Growth and Limits
9.5 Analyzing Algorithm Running Time
9.6 Analyzing Comprehensions and While Loops
9.7 Analyzing Built-In Data Type Operations
9.8 Worst-Case Running Time Analysis
9.9 Testing Functions IV: Efficiency
10. Abstraction, Classes, and Software Design
10.1 An Introduction to Abstraction
10.2 Defining Our Own Data Types, Part 3
10.3 Defining Our Own Methods
10.4 Data Types, Abstract and Concrete
10.5 Stacks
10.6 Exceptions as a Part of the Public Interface
10.7 Queues
10.8 Priority Queues
10.9 Defining a Shared Public Interface with Inheritance
10.10 The object Superclass
11. Case Study: Building a Simulation
11.1 The Problem Domain: Food Delivery Networks
11.2 Object-Oriented Modelling
11.3 A “Manager” Class
11.4 Food Delivery Events
11.5 Creating a Discrete-Event Simulation
[CSC111H]
Assignment 1 - February 1, 2023
Blockchain
Total Mark 44 / 44 (100%)
In this assignment, I worked on conceptual application of linked lists to a popular and novel area of computing: blockchain and cryptocurrencies.

Handout
Assignment 2 - March 1, 2023
Wordle AI
Total Mark 55 / 55 (100%)
Worked on two-player variation of Wordle called Adversarial Wordle with implementation of artificial intelligence. I applied fundamental application of trees: representing the state of a system, and branching decisions that lead from one state to another.

Handout
Assignment 3 - March 22, 2023
Graphs & Networks
Total Mark 60 / 60 (100%)
Using graph abstract data type, I worked on the problem domain of interconnection networks. The assignment involved Ring topology, Torus topology, Star topology, and Routing Algorithms like Shortest-Path Ring Network, Shortest-Path Torus Network, and Shortest-Path Star Network. Finally, I worked on Interconnection Network Discrete-Event Simulation and Greedy Channel Routing Algorithm as well as Greedy Path Routing Algorithm.

Handout
What I've Learned
Below are some materials that I learned from CSC111. For additional information, please visit Course Notes.
12. Interlude: Nifty Python Features
12.1 Sequences Revisited: Ranges, Indexing, and Slicing
12.2 String Interpolation with f-strings
12.3 Functions with Optional Parameters
13. Linked Lists
13.1 Introduction to Linked Lists
13.2 Traversing Linked Lists
13.3 Mutating Linked Lists
13.4 Index-Based Mutation
13.5 Linked List Running-Time Analysis
14. Induction and Recursion
14.1 Proof by Induction
14.2 Recursively-Defined Functions
14.3 Introduction to Nested Lists
14.4 Nested Lists and Structural Recursion
14.5 Recursive Lists
14.6 Application: Fractals
15. Trees
15.1 Introduction to Trees
15.2 Recursion on Trees
15.3 Mutating Trees
15.4 Running-Time Analysis for Tree Operations
15.5 Introduction to Binary Search Trees
15.6 Mutating Binary Search Trees
15.7 The Running Time of Binary Search Tree Operations
16. Case Study: Abstract Syntax Trees
16.1 Introduction to Abstract Syntax Trees
16.2 Variables and the Variable Environment
16.3 From Expressions to Statements
16.4 Abstract Syntax Trees in Practice
17. Graphs
17.1 Introduction to Graphs
17.2 Some Properties of Graphs
17.3 Representing Graphs in Python
17.4 Connectivity and Recursive Graph Traversal
17.5 A Limit for Connectedness
17.6 Cycles and Trees
17.7 Computing Spanning Trees
17.8 Application: Control Flow Graphs
18. Sorting
18.1 Sorting Lists and Binary Search
18.2 Selection Sort
18.3 Insertion Sort
18.4 Introduction to Divide-and-Conquer Algorithms
18.5 Mergesort
18.6 Quicksort
18.7 Running-Time Analysis for Mergesort and Quicksort
18.8 Application: Scheduling Events
18.9 Generalized Sorting
19. Average-Case Running Time (optional reading)
19.1 Introduction to Average-Case Running Time
19.2 Average-Case Running Time of Linear Search
![]()




